Java EE7 and Maven project for newbies - part 1 - a simple maven project structure - the parent pom
Series
Why ?
Many times, I am trying to resolve several basic or complex Maven / Java EE project structure issues, on my day work. In order to provide the solutions, I often end up experimenting with the project structure, test my deployment on different application servers and fine grain my configuration. Maven can have a steep learning curve for newcomers and if you add in the mix the sometimes complex configuration requirements of a modern Java EE application, the things get more frustrating. I have also seen in my career, that lots of junior java developers, when they join a big team or project, most of the times the project structure is already fine grained and configured for them by more senior members. They assume that it works, and they don't spent time to understand the wiring and configuration. I have done this mistake myself in the past. They are being assigned simple coding tasks and they deep dive on requirements but unfortunately they forget to study the application structure.Their senior colleagues forget as well to train them on this particular area, most of the times due to time restrictions. This may lead to accidents when people start messing around with the structure of the application with no previous experience, while trying to make it_ work_. Maven and it's conventions aim to help a lot on establishing common structures and conventions on how a project should be structured, but the again you need to understand the tool, the conventions and finally master your configuration.
You can often hear someone saying I added this library there and it worked, if you reply define there, then you might get some interesting answers. Sometimes by accident or luck it works but in a complex multi-module application, most of the times it just works is an understatement and problems will start appearing soon enough.
This series of posts is targeting Maven and Java EE newcomers mostly, but feel free to share or use it as a demo if you are a more senior developer. I am going to attack on a demo basis some real problems I happen to discover from day to day work and try to provide solutions while providing a basic explanation or links to related resources. Please feel welcome to add comments, corrections or references for something that can be performed / completed in a far cleaner way. The best way to learn Maven and create a complex but easy to maintain application is to start from scratch, empty pom files.
The main message I am trying to pass along to junior developers reading my posts is that studying_ your application structure, asking about the underlying build tools is part of your work and you should never assume that someoene else is always going to take care of it.It is also a stepping in order to challenge more difficult tasks and improve your skills as a Java developer.
Core technologies to be used
- Java EE 7 based application
- Will be packaged as an EAR
- Will be featuring multiple components (wars, jars, ejb jars)
- Will be compiled towards Java 7
- Will be packaged using Maven 3
My demo ear application
My application is going to be an EAR, for this particular post, this ear is going to include 2 top level modules a war and an ejb-jar. There is also going to be a jar, that will contain the classes that will be my database domain model (JPA entities). I am going to expand the structure adding more resources in future posts. A very abstract image just to give an idea, illustrating what are going to 'include in our ear'. The war module in the future will contain servlets or jsf compoments, the services module is going to contain a set of common Stateless Sesson Beans (or Message Driven Beans). The domain project is going to have plain Java classes properly annotated with JPA2 constructs.
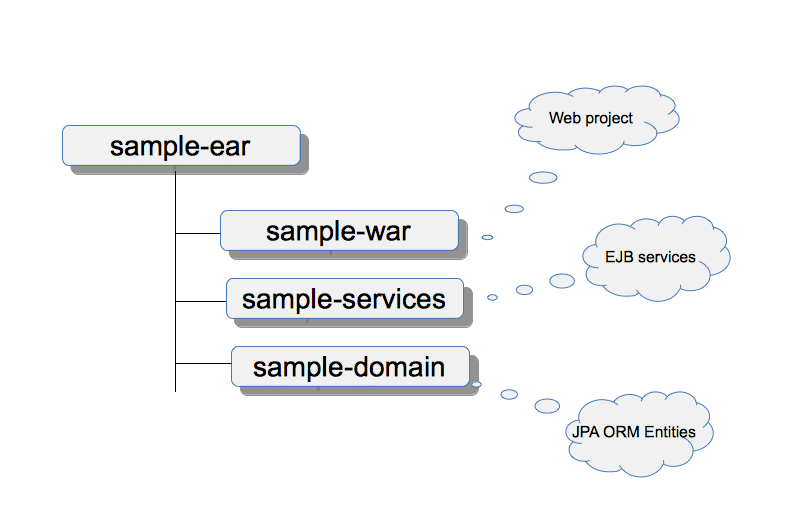
Composing the basic structure of our application using Maven
In order to build the ear above we need to define modules and the parts of our application, using Maven which is anyway our building/packaging/configuration tool. This is one of the most steps and if you get this from the start then the rest will be simple technicalities or configuration specifics. What I am proposing is not the ultimate solution but something very close to the standard which is most of the times the way to go if you start a new app, so no funcy specifics here, let's follow the standard and start building on a concrete foundation.
So let's forget the image above at the moment and let's think Maven, what and how many modules may define, how to interconnect them and define dependencies. Note, my proposed way of work is the standard but it is not the ultimate solution, meaning you can achieve the same results by packaging your application as an ear, define fewer modules and dependencies. Let's assume that I want to cover highly complex structures so I will define a generic structure, always following the standards.
I assume that you have covered some basic stuff from Maven and you are at least familiar with the terminology. If not have a look here.
Remember Maven is about, placing your files to the right places according to a well defined structure , and defining the maven plugins, which are some kind of tools to do specific things compile, package, copy files, etc. The plugins are being invoked by Maven, so yes again you need to define the plugins to the correct place and with the appropriate configuration. You are not writing your make or ant scripts, you just insert plugins and ask maven to execute them in a well define order.
As good ex-colleague of mine (wrote in a email recently), it is good to break conventions in your life and in your coding, but never with Maven. He is right :) .
If you are not sure how to install maven, have a look here Windows or Mac
My Maven Project Structure - Abstract
We are building with Maven, so we need to think in terms of maven pom (s) and modules. In order to create out required ear packaging (see above) we need 5 poms
- A pom - acting as a parent
- A pom that will contain/define the final ear - responsible for configuring the final package.
- A pom that will contain/define the code of the web application, meaning our .war
- A pom that will contain/define the code of the ejb-module, the module that we are going to package our EJB(s)
- A pom that will contain the classes that are going to be our JPA (Database Entities)
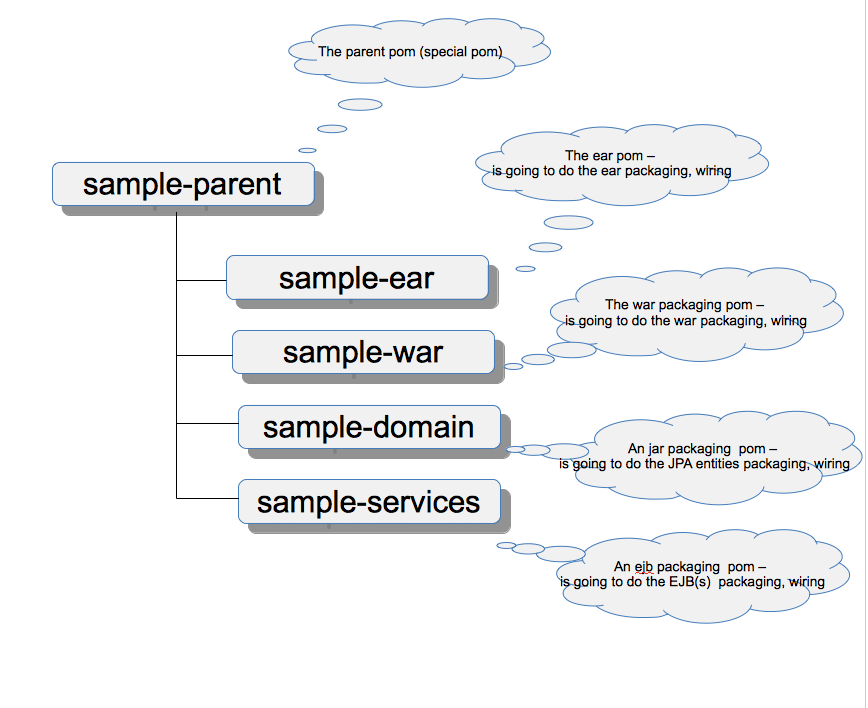
As you can see, every module has it's own pom, and there is the parent, one of the things that still lot's of people do not add in their structure, assuming that they don't need it, since their project is small, and the after a while while more modules are being added, you end up with havoc. So make a note here the parent pom is really nice to have and configure'. This is the pom where you define all your dependency versions (that is libraries) and you configure the maven plugins, so that all the child poms, inherit a common configuration.
My Maven Project Structure - the Parent pom
As I have already elaborated we are going to start from scratch, so I am creating a new folder called sample-parent and in this folder I add a new file called pom.xml'.
Yeap not excited, just make note on the packaging element which is defining pom'.The parent is called parent, because it defines and manages the children modules, this is done in the modules definition section. Our original pom becomes something like that. That means that we must create the related folders under our sample-parent, and then add a pom.xml to each one of them.
Let's continue adding some more configuration. This is an important section since we define versions for
- the maven plugins we are going to use and configure
- any libraries - dependencies used and reference from other modules
- other generic properties, like the version of the Java runtime we are going to compile
- The default encoding for source files or other assets.
Let's add after the properties section, another important one, the ** dependencyManagement** .This is where we will define the dependencies and their versions that can be potentially used in our application modules. In this section we actually care about the version, the inclusion or exclusion of the dependencies it is up to the child pom (meaning they are not added automatically), their scope as well. So the DependencyManagement section is the one to control, in one central place the versions.
Another last but important section in our parent pom is similar to dependencyManagemt is called pluginManagement, and is the section where we will define, the versions and common configuration of all the maven plugins that are going to referenced and used during our application configuration and packaging.In the sample below I have defined one of the most basic, the compiler plugin, but of course I am going to need more!
Let's add and configure some more plugins that we are going to use later on.Add those within the plugin management section. We define the ejb plugin that is going to compile and package our ejb(s) and the war plugin that is going to package our war.
That's for now
You can download our minimal sample here (tag post1, bitbucket). At the time being, it seems that we have not completed anything, but eventually defining a clean and concrete parent pom, is going to be the basis for the rest of the work we are going to do in the upcoming posts.
Points to study
- the maven standard layout
- the parent pom
- the importance of dependencyManagement & pluginManagement
Continue to part2
References
- Maven3
- Java EE 7 Tutorial
- The Maven project structure
- The parent pom
- What is dependency Management?
- What is plugin management?
- You can download the above code here.